Yes, cryptocurrencies are the future of finance, and in this article, we will explain why. Bitcoin emerged amidst growing distrust of traditional financial institutions and the desire for greater financial autonomy.
Bitcoin was created in 2009 as a response to the global financial crisis that resulted from the collapse of the real estate market in the United States in 2008. This was caused by banks issuing risky subprime mortgages and the functioning of complex instruments based on these loans.
In simple terms, investment firms were selling toxic worthless debt as securities. When property prices began to fall and borrowers could no longer afford their payments, many financial institutions collapsed. As a result, the US government bailed out the banks by issuing currency, meaning that all citizens paid for it. The recession affected economies worldwide.
Bitcoin’s creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, directly referenced these events by including the title from the newspaper “The Times” in the first Bitcoin block, known as the genesis block.
.

He expressed the belief that it was necessary to break the link between currency and institutions. Bitcoin was intended to protect people from betrayal, fraud, and monopolization by financial institutions. The decentralized nature of Bitcoin was meant to counterbalance traditional financial systems, enabling fast, anonymous, and secure peer-to-peer transactions (directly between interested parties, without the involvement of a trusted third party).
Bitcoin was designed to protect against crises and inflationary policies. Inflation is considered a hidden tax that most affects the poorest. It has long been argued that traditional financial institutions would attempt to integrate and control cryptocurrencies, which is contrary to their fundamental values. And indeed, this has happened – cryptocurrency technology has been co-opted, and banks are creating their own digital currencies, known as CBDC (Central Bank Digital Currency).
It follows undeniably that cryptocurrencies are the future of finance. Another question should be asked: which cryptocurrencies to choose: government-backed or anti-government?
Anti-establishment
Bitcoin was designed in such a way that its functioning is inherently anarchistic and anti-government. Blockchain, the technology behind Bitcoin, is a manifestation of freedom of speech and financial sovereignty. The Declaration of Bitcoin Independence emphasizes that it is independent of all power structures and does not require recognition or regulation. It is a currency meant to operate outside the system, eliminating the need for intermediaries and third-party interference, including tax authorities. Bitcoin is a tool that allows the direct transfer of economic power between individuals, representing a fundamental change in how finance operates.
Quoting the Declaration of Bitcoin Independence: “The intrusiveness of third parties is eliminated; it is purely P2P.” The blockchain is freedom of speech Bitcoin is decentralized, voluntary, non-aggressive, and it doesn’t aim to operate within the current system. Bitcoin doesn’t need recognition, integration, regulation, or taxation from power institutions. Bitcoin doesn’t bow to power structures. It undermines them”.
The value of Bitcoin and Metcalfe’s law
The creator of Ethernet technology, computer scientist Prof. Robert Metcalfe, formulated a law regarding the utility of teleinformatics systems, which states:
“The utility of a telecommunications network or other teleinformatics system grows proportionally to the square of the number of devices/users connected to it. […] An example illustrating the operation of such a law in practice is the mobile phone network. If such a network had only one user, carrying a mobile phone would make no sense. The second person already builds minimal value because you can finally call someone. Another thousand people create new opportunities for interactions with people we don’t know yet.” When the mobile phone network covers the entire planet and half the population has their own phone number, the value of such a network is gigantic and grows exponentially with its users. […] This means in practice that the larger the network of users, the greater the value of that network. According to Metcalfe’s law, the value of a network depends on the square of the number of possible connections between participants” [2].
.
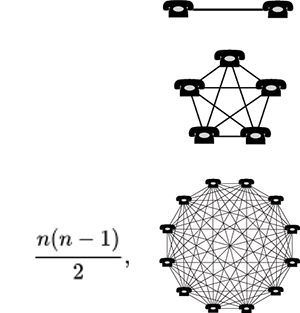
In the context of Bitcoin, Metcalfe’s law, which states that the value of a network grows proportionally to the square of the number of users, is hugely significant. The larger the network of users, the greater the value of Bitcoin. However, a key element is also the controlled supply, which halves in halving cycles.
It is this combination of factors, limited supply and increasing demand, that drives the rise in Bitcoin’s value and makes it one of the most important assets in today’s financial world.
Banking policies
The growing demand is influenced by macroeconomic factors. Central bank policies, especially inflationary ones, have influenced the perception of Bitcoin as a hedge against the devaluation of traditional currencies. Bitcoin was meant to protect people from the effects of irresponsible monetary policy. In the face of rising inflation and falling trust in fiat currencies, Bitcoin has gained popularity as a form of capital protection.
Central banks around the world pursue policies of low interest rates and massive money printing, leading to the depreciation of traditional currencies. In this context, Bitcoin is seen as “digital gold,” which can protect against inflation and provide stability of value in the long term.
Bitcoin was created in response to the crisis and naturally began to be seen as a so-called Safe Haven, or a safe harbor in difficult times. It didn’t take long for reality to validate the economic determinants of Bitcoin’s creation. Central bank policies and the resulting attack on private property formed the basis of the first significant macroeconomic event in Bitcoin’s history, which was intended to protect people from crises and inflationary policies.
The decline in trust in financial institutions verified the ideological assumptions of Bitcoin and proved to have a significant impact on its valuation.
The crisis in Cyprus in 2013 led the country to bankruptcy. Cyprus was forced by the European Union and the International Monetary Fund to tax ordinary citizens’ deposits, initially considering the confiscation of 80% of deposits. The German finance minister commented at the time: “Realistically speaking, very little will be returned.” Ultimately, however, they decided to confiscate 47.5%. Bankier.pl wrote about the events as follows: “47.5% – that’s how much will disappear from bank accounts in Cyprus with funds exceeding 100,000 euros. ‘Haircut’ obejmie klientów restrukturyzowanego Bank of Cyprus i likwidowanego banku Laiki” [3]. Banks introduced withdrawal and transfer restrictions.
As K. Piech notes: “Knowledge and technological progress have not been unambiguously and definitively included in economic growth models. These models increasingly include technology (including the internet) as part of the broader concept of knowledge, but this concept has not (yet) been expressed in a measurable way. The broad concept of knowledge as a factor in economic growth also includes education and innovation. Despite the Solow paradox and the bursting of the ‘internet bubble,’ knowledge and technological progress, including teleinformatics, have already played a role not only in real economic events but also in theoretical achievements and empirical research. Although the ‘new economy’ turned out to be just another episode in the economic history of the world, full of stock market speculation and financial crashes (especially in the 19th and early 20th centuries), it does not mean that technologies do not impact economic growth” [4].
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC)
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) are digital counterparts of traditional currencies issued by central banks. Their foundations are based on technology known from cryptocurrencies, but they stand in contrast to them because the blockchains used by CBDC are entirely closed within institutions.
It is believed that CBDC can revolutionize financial systems, offering safer, more convenient, and efficient methods of conducting transactions. They can also increase access to financial institutions, especially in underdeveloped countries where the majority of the population does not even have a bank account. CBDC will also change the way banks conduct monetary policy, enabling them to have direct control over the money supply (inflation).
All this comes at the cost of privacy.
Issued and controlled by central banks, CBDC are centralized, meaning they can be monitored and tightly regulated by governments. This opens the door to potential privacy violations and restrictions on the financial freedom of users, which contradicts the fundamental values of Bitcoin. While Bitcoin symbolizes financial independence, CBDC are a tool of monetary policy that can be susceptible to inflation and central control.
The Future of Finance and Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies, thanks to their decentralized nature, are changing the face of global finance. They enable autonomous transactions without the need for financial institution intermediaries. The decentralization of the Bitcoin network brings benefits such as:
- security
- financial autonomy
- transparency
- transaction speed.
The nature of CBDC, although based on the same technology, is centralized. CBDC aim to combine the features of cryptocurrencies with the possibility of control and stabilization. Their main advantages are listed as:
- stability
- efficiency
- control.
Technological progress, including the development of blockchain, will be a key factor influencing the future of cryptocurrencies. Blockchain technology, on which cryptocurrencies are based, is one of the most important innovations of the 21st century. Blockchain allows for the creation of immutable and transparent transaction records, which has enormous potential in various sectors of the economy, not just in finance. Some possible applications include:
- Smart Autonomous Contracts: self-executing contracts that automate and secure agreements between parties without the need for intermediaries.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): a financial ecosystem that operates entirely on the blockchain, offering services such as loans, deposits, and trading without traditional financial institutions.
CBDCs also leverage advanced technologies to meet the demands of modern financial systems. Examples of innovations in the area of CBDCs include:
- Integration with existing financial systems: CBDCs can be easily introduced into current banking and payment systems, facilitating their adoption.
- Security and privacy: Although CBDCs are centralized, technologies are being developed to ensure high standards of security and user privacy protection.
Conclusions and summary
Cryptocurrencies, both like Bitcoin and CBDCs, will become the future of finance. It will depend on us – the users – whether we side with the decentralized nature and independence or with strictly controlled currencies.
Bitcoin, as the pioneer among cryptocurrencies, has shown that it is possible to create an independent financial system that operates outside the control of governments and institutions. Its success has paved the way for other cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies, which can revolutionize the world of finance. As more people and institutions adopt cryptocurrencies, their role in the global financial system will increase, potentially leading to fundamental changes in how we manage our finances.
________________________________________
Sources:
[1] https://cyfrowaekonomia.pl/deklaracja-niepodleglosci-bitcoina/
[2] M. Grzybkowski, S. Bentyn, Kryptowaluty, Wydawnictwo Crypto-logic, Poznań 2018, s. 188.
[4] K. Piech, Technologie, edukacja i innowacje w teoriach wzrostu gospodarczego, published in: Polityka Gospodarcza, nr 9, 2004 r., s. 154.
